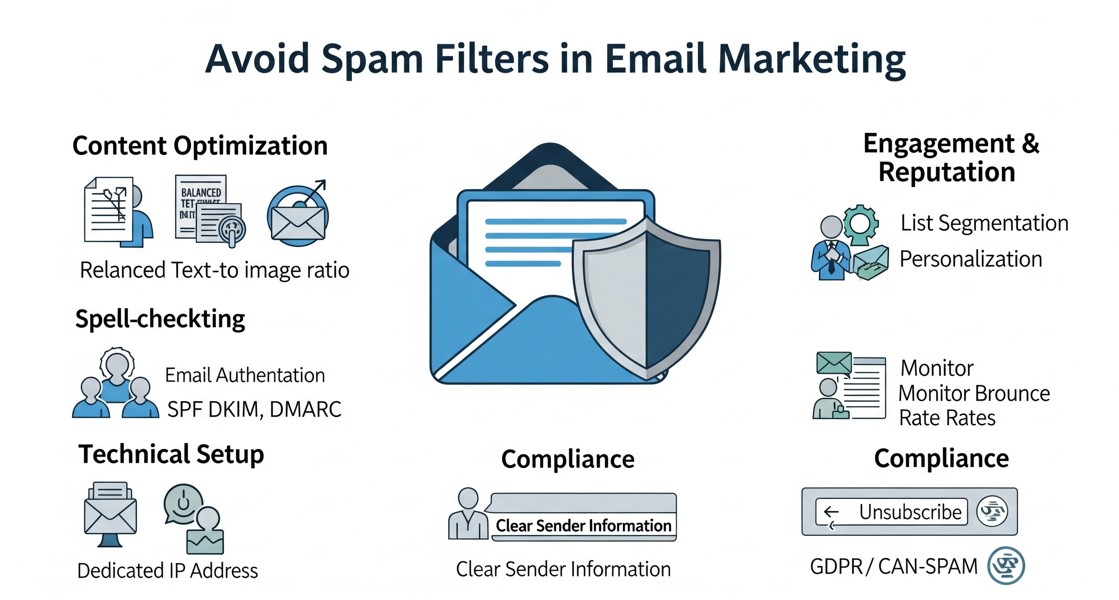
This guide explains how to avoid spam filters by improving email authentication, sender reputation, content quality, and list hygiene. It offers practical strategies to boost deliverability, reach inboxes consistently, and maximize the success of email marketing campaigns.
Your carefully crafted email campaign is ready to launch. You’ve spent hours perfecting the subject line, designing the layout, and writing compelling copy. But there’s one major hurdle standing between you and your audience’s inbox: spam filters.
Spam filters have become increasingly sophisticated, protecting users from unwanted messages but sometimes catching legitimate marketing emails in the process. For email marketing professionals, understanding how to navigate these digital gatekeepers is crucial for campaign success.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through proven strategies to keep your emails out of spam folders and ensure your messages reach their intended recipients. From technical configurations to content optimization, you’ll learn actionable techniques that can dramatically improve your email deliverability rates.
Understanding How Spam Filters Work

Spam filters use complex algorithms to evaluate incoming emails based on multiple factors. These systems analyze everything from your sender reputation to the content within your messages, assigning each email a spam score. If that score exceeds a certain threshold, your email gets filtered out before it reaches the recipient.
Modern spam filters consider dozens of variables simultaneously. They examine your IP address reputation, domain authentication, content patterns, recipient engagement history, and even the time you send your emails. Machine learning algorithms continuously evolve these filters, making them more accurate at detecting unwanted messages while occasionally catching legitimate emails.
The challenge for marketers lies in the fact that these filters operate differently across email providers. Gmail’s algorithm differs from Outlook’s, which differs from Yahoo’s. What passes through one filter might get caught by another, making it essential to optimize for multiple systems.
Authentication: Your First Line of Defense
Email authentication serves as your digital passport, proving to receiving servers that you are who you claim to be. Without proper authentication, even the most well-intentioned email marketing campaigns can end up in spam folders.
Setting Up SPF Records
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records tell receiving email servers which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. Think of it as a guest list for your domain’s email privileges.
To set up SPF, you’ll need to add a TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings. A basic SPF record might look like: v=spf1 include:mailchimp.com ~all if you’re using Mailchimp as your email service provider. The “~all” part indicates a soft fail for unauthorized senders, while “-all” would indicate a hard fail.
Implementing DKIM Signatures
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) adds a digital signature to your emails, allowing receiving servers to verify that your message hasn’t been tampered with during transmission. Most email service providers handle DKIM setup automatically, but you’ll need to add their DKIM record to your DNS settings.
Enabling DMARC
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) builds on SPF and DKIM, providing additional protection against email spoofing. A DMARC policy tells receiving servers what to do with emails that fail authentication checks.
Start with a monitoring-only DMARC policy (p=none) to observe how your emails perform, then gradually move to quarantine (p=quarantine) or reject (p=reject) policies as you gain confidence in your setup.
Building and Maintaining Sender Reputation
Your sender reputation acts like a credit score for your email marketing efforts. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) track how recipients interact with your emails, using this data to determine whether future messages should reach the inbox or spam folder.
Sender reputation depends heavily on engagement metrics. High open rates, click-through rates, and low complaint rates signal to ISPs that recipients want your emails. Conversely, low engagement or high bounce rates can damage your reputation quickly.
Consistency plays a crucial role in maintaining a good sender reputation. Sudden spikes in sending volume or dramatic changes in content style can trigger spam filters. Gradually increase your sending volume when launching new campaigns, and maintain consistent sending patterns over time.
Monitor your sender reputation using tools like Google Postmaster Tools, Microsoft SNDS, or third-party services like Sender Score. These platforms provide insights into how ISPs view your sending practices and alert you to potential issues before they impact your campaigns.
Content Optimization Strategies
The content of your emails significantly influences whether they reach the inbox. Spam filters analyze both text and HTML elements, looking for patterns commonly associated with unwanted messages.
Crafting Spam-Free Subject Lines
Your subject line serves as the first impression for both recipients and spam filters. Avoid ALL CAPS text, excessive punctuation marks, and spam trigger words like “FREE,” “GUARANTEED,” or “ACT NOW.” Instead, focus on creating compelling, descriptive subject lines that accurately reflect your email content.
Keep subject lines between 30-50 characters for optimal display across devices. Personalization can improve open rates, but avoid generic personalization that feels automated. “Hey [First Name], check this out!” is less effective than incorporating meaningful personalization based on recipient behavior or preferences.
Balancing Text and Images
Heavy image-to-text ratios can trigger spam filters. Aim for a balanced approach where text content comprises at least 60% of your email. When using images, always include descriptive alt text, as some email clients block images by default.
Avoid embedding text within images, as spam filters cannot read this content and may view image-heavy emails suspiciously. If you must include text in images, ensure your email contains sufficient plain text content to maintain a proper balance.
Avoiding Spam Trigger Words
Certain words and phrases commonly appear in spam messages, causing filters to flag emails containing them. Beyond obvious culprits like “FREE” and “GUARANTEED,” be cautious with words like “urgent,” “limited time,” “exclusive offer,” and “click here.”
Context matters as much as the words themselves. Using “free” in “free shipping” is generally acceptable, while “FREE MONEY” is likely to cause problems. Focus on natural, conversational language that provides genuine value to your recipients.
List Hygiene and Management
Clean email lists are fundamental to avoiding spam filters. Poor list hygiene not only hurts deliverability but can also damage your sender reputation permanently.
Implementing Double Opt-In
Double opt-in requires subscribers to confirm their email address by clicking a link sent to their inbox after initial signup. While this process may reduce your initial signup numbers, it significantly improves list quality and engagement rates.
Subscribers who complete double opt-in are more likely to engage with your emails, leading to better deliverability over time. This process also protects you from fake email addresses and reduces the risk of spam complaints.
Regular List Cleaning
Remove inactive subscribers regularly to maintain healthy engagement metrics. Define inactive subscribers based on your sending frequency—if you send weekly emails, consider subscribers who haven’t engaged in 3-6 months as inactive.
Before removing inactive subscribers entirely, try a re-engagement campaign. Send a special offer or simply ask if they want to continue receiving your emails. This approach can reactivate some subscribers while providing clear consent to remove others.
Managing Bounce Rates
Hard bounces occur when emails are sent to invalid addresses, while soft bounces result from temporary issues like full mailboxes. Remove hard bounces immediately, as high bounce rates can quickly damage your sender reputation.
Most email service providers handle bounce management automatically, but monitor these metrics closely. Bounce rates above 2% indicate potential list quality issues that need immediate attention.
Technical Configuration Best Practices
Beyond authentication and content, several technical factors influence email deliverability. These behind-the-scenes elements can make the difference between inbox placement and spam folder relegation.
IP Warming and Reputation
If you’re using a dedicated IP address for sending emails, warm it up gradually. Start with small volumes to highly engaged subscribers, then slowly increase volume over several weeks. This process helps establish a positive reputation for your IP address.
Shared IP addresses, while managed by your email service provider, still require attention to your sending practices. Poor practices from one sender can affect all users on a shared IP, making it crucial to follow best practices consistently.
Monitoring Blacklists
Various organizations maintain blacklists of IP addresses and domains associated with spam. Regularly check if your sending IP or domain appears on major blacklists like Spamhaus, Barracuda, or Validity.
If you find yourself blacklisted, follow the delisting procedures promptly. Most blacklist providers offer clear instructions for removal, though the process may take several days to complete.
Timing and Frequency Optimization
When and how often you send emails can impact spam filter treatment. Sudden changes in sending patterns or inappropriate timing can trigger suspicious activity alerts.
Send emails at consistent times when your audience is most likely to engage. Analyze your email analytics to identify optimal sending times for your specific audience, as general “best practice” times may not apply to your subscribers.
Respect frequency preferences by allowing subscribers to choose how often they hear from you. Overwhelming subscribers with too many emails increases unsubscribe rates and spam complaints, both of which hurt your sender reputation.
Testing and Monitoring Your Campaigns
Regular testing helps identify potential deliverability issues before they impact your entire list. Use these strategies to monitor and optimize your email marketing performance.
Deliverability Testing Tools
Services like Mail Tester, GlockApps, or 250ok allow you to test your emails against multiple spam filters before sending to your full list. These tools provide detailed reports on potential issues and suggestions for improvement.
Send test emails to seed accounts across major email providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo) to monitor where your emails land. Create accounts specifically for this purpose and check them regularly to ensure consistent inbox placement.
Analyzing Campaign Metrics
Monitor key metrics beyond open and click rates. Pay attention to spam complaint rates (should be below 0.1%), unsubscribe rates, and inbox placement rates. Declining metrics often indicate developing deliverability issues.
Use your email service provider’s analytics to identify trends over time. Gradual decreases in open rates might indicate reputation issues, while sudden drops could signal technical problems or list quality concerns.
Choosing the Right Email Service Provider

Your email service provider plays a crucial role in deliverability success. Not all providers offer the same level of deliverability support or reputation management.
Look for providers that offer robust authentication setup, dedicated IP options, and comprehensive analytics. They should provide deliverability monitoring tools and have established relationships with major ISPs.
Consider providers with strong anti-spam policies that actively monitor their users’ sending practices. While this might seem restrictive, it helps maintain a good platform-wide reputation that benefits all users.
Maximizing Your Email Marketing Success

Avoiding spam filters requires ongoing attention to technical setup, content quality, and list management. The strategies outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive foundation for improving your email deliverability rates.
Start by implementing proper authentication protocols and cleaning your email list. Focus on creating valuable, engaging content that your subscribers genuinely want to receive. Monitor your metrics regularly and adjust your approach based on performance data.
Remember that email deliverability is not a one-time setup but an ongoing process. Stay informed about industry changes, test your campaigns regularly, and maintain the high standards that both your subscribers and ISPs expect. With consistent effort and attention to best practices, you can ensure your email marketing messages reach their intended recipients and drive the results your business needs.
FAQ: Avoiding Spam Filters in Email Marketing
1. Why do legitimate marketing emails end up in spam folders?
Legitimate emails can land in spam folders due to poor sender reputation, missing authentication records, low engagement rates, spam-like content, or technical misconfigurations. Even small issues such as sudden spikes in sending volume or outdated email lists can trigger spam filters.
2. What is email authentication and why is it important?
Email authentication verifies that your emails are genuinely sent from your domain and have not been altered in transit. Protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC help email providers trust your messages, significantly improving inbox placement and protecting your brand from spoofing and phishing.
3. How does sender reputation affect deliverability?
Sender reputation is based on how recipients interact with your emails over time. High open rates, clicks, and low spam complaints signal trust, while high bounce rates, low engagement, or frequent complaints damage reputation and increase the chance of emails being filtered as spam.
4. Do subject lines really impact spam filtering?
Yes, subject lines are heavily analyzed by spam filters. Excessive capitalization, misleading language, aggressive sales terms, or spam trigger words can increase spam scores. Clear, honest, and relevant subject lines tend to perform better and build long-term trust.
5. What role does email content play in spam filtering?
Spam filters evaluate both text and HTML structure. Emails with excessive images, very little text, broken code, or unnatural language patterns are more likely to be flagged. Well-balanced content with clear messaging and value-driven copy improves deliverability.
6. How often should I clean my email list?
Email lists should be reviewed regularly, ideally every three to six months. Removing inactive subscribers, invalid addresses, and hard bounces helps maintain engagement metrics and protects sender reputation from long-term damage.
7. Is double opt-in really necessary?
While not mandatory, double opt-in greatly improves list quality. It ensures subscribers genuinely want your emails, reduces fake or mistyped addresses, lowers spam complaints, and leads to better engagement and deliverability over time.
8. Can sending too many emails hurt deliverability?
Yes, sending emails too frequently can overwhelm subscribers, increasing unsubscribe and spam complaint rates. Consistent frequency aligned with subscriber expectations helps maintain engagement and keeps spam filters from flagging your campaigns.
9. How can I test emails before sending them to my full list?
You can use deliverability testing tools and seed email accounts across major providers to see where emails land. Testing helps identify spam-related issues, authentication problems, or formatting errors before launching large campaigns.
10. How long does it take to improve email deliverability?
Improving deliverability is a gradual process. While technical fixes like authentication can show results quickly, rebuilding sender reputation through consistent engagement and clean practices may take several weeks to months.


















No Comments